
A brief introduction to the basic knowledge of electrical control cabinet
The electrical control cabinet is an indispensable core device in industrial automation and power systems. By integrating various electrical components, it achieves centralized control, protection, and monitoring of circuits. As the “nerve center” of modern industry, the performance of the electrical control cabinet directly affects the stability and safety of the production system. This article will systematically analyze the technical key points of the electrical control cabinet from aspects such as basic concepts, core components, working principles, and design specifications.


Definition and function of electrical control cabinet:
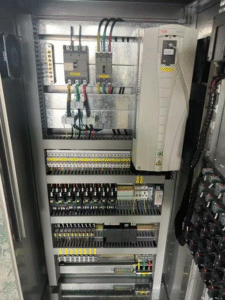
An electrical control cabinet is a sealed metal enclosure housing circuit breakers, contactors, relays, PLCs (Programmable Logic Controllers), and other electrical components. It receives and distributes electrical power while performing logic control over actuators such as motors and lighting equipment. Its core functions include:
1. Power Distribution: Allocates main power to branches efficiently to prevent overload.
2. Circuit Protection: Prevents faults like short circuits and overloads through fuses and thermal relays.
3. Signal Processing: Transforms input signals from sensors and switches into control commands to drive actuators.
4. Status Monitoring: Displays operational status via integrated indicators and instruments for easy troubleshooting.
Core component analysis:
1. Power Modules Main Circuit Breaker: Acts as the main power switch, providing overload and short-circuit protection. Isolation Transformer: Provides safe voltage and isolates grid interference. Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS): Maintains critical equipment operation during power outages.
2. Control Components Contactors: Controlling high-current circuits through electromagnetic latching, commonly used for motor start-stop operations. Relays: Achieving high-current control through low-current signals, performing logic conversion (e.g., time-based or temperature-controlled). PLC: Programmable Logic Controller that implements complex automation logic via ladder diagram programming.
3. Protection Devices Fuses: Instantly interrupting severe overloads or short-circuit currents. Thermal Relays: Detecting motor overload through bimetallic deformation to prevent burnout. Surge Protectors: Suppressing transient overvoltages caused by lightning strikes or grid fluctuations.
4. Human-Machine Interface Buttons and Indicators: Manual operation and status display. Touchscreen (HMI): Real-time data monitoring and parameter modification. Instruments: Voltage meters, ammeters, etc., providing intuitive electrical parameter visualization.


Working principle and logical flow:
The electrical control cabinet operates through a three-step “input-processing-output” mechanism:
1. Input stage: Sensors and switches convert physical signals (e.g., temperature, pressure) into electrical signals.
2. Processing stage: PLCs or relays process these signals according to predefined logic to generate control commands.
3. Output stage: Actuators like contactors and frequency converters drive load components such as motors and valves to perform operations.
Design specifications and safety standards:
1. Cabinet Structure Protection Rating: The IP rating (e.g., IP54) indicates dust and water resistance, which should be selected according to environmental conditions. Cooling Design: Implement forced air cooling or natural ventilation to prevent component aging caused by high temperatures. Wiring Specifications: Separate power and low-voltage circuits using cable trays with clearly labeled wire numbers.
2. Safety Standards Grounding Protection: Ensure reliable grounding of the cabinet and components to prevent electric shock. Emergency Stop Button: Immediately cut off all power in emergencies. Labeling System: Standardize component labeling and circuit diagram attachment for easy maintenance.
As the cornerstone of industrial automation, electrical control cabinets require designs that balance functionality and safety. With the advancement of Industry 4.0, intelligent control cabinets integrating IoT and edge computing are becoming the new norm, yet fundamental principles remain the bedrock of technological evolution. Mastering core knowledge of electrical control cabinets is essential for professionals in electrical engineering, automation maintenance, and related fields.

Our company provides high quality and stable products, including reverse osmosis system, sludge dewatering machine, mechanical grille, dosing device, electrical control cabinet, etc., our professionals will provide you with installation, commissioning, operation, and follow-up maintenance services to help you solve problems!
Yixing Shenghe Environmental Protection Co., Ltd.

IPv6 network supported